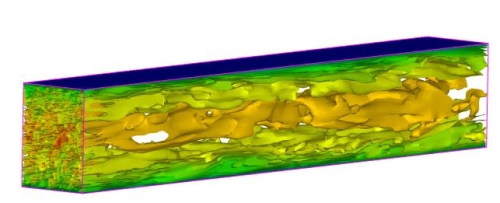
BACKGROUND
LES is an appropriate method for flows that include turbulent fluctuations with large spatial scales.
For this type of flow, a fairly coarse mesh can be used to resolve the large fluctuations. RANS in this type
of flow is often a poor alternative, since the large fluctuations are difficult to accurately model with
a RANS turbulence model. The problems for LES start when walls are introduced. The reason is that
length scales of the largest fluctuations near walls are not large;
hence a fine mesh must be used to resolve these fluctuations.
PROJECT
Navier-Stokes (PANS) modelling method is presented, which incorporates
improved asymptotic representation in near-wall turbulence modelling. The
effect of near-wall viscous damping can thus be better accounted for in
simulations of wall-bounded turbulent flows. The proposed LRN PANS model
uses an LRN k-eps model as the base model and introduces directly its model
functions into the PANS formulation. As a result, the inappropriate
wall-limiting behavior inherent in the original PANS model is corrected.
An interesting feature of the PANS model is that the turbulent Prandtl
numbers in the k and eps equations are modified compared to the base model.
It is found that this modification has a significant effect on the modelled
turbulence. The proposed LRN PANS model is scrutinized in computations of
decaying grid turbulence, turbulent channel flow and periodic hill flow.
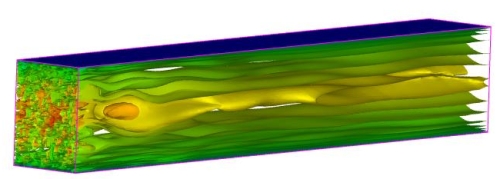
U velocity contours for fk=0.4

REFERENCES
-
J.M. Ma, L. Davidson, S.-H. Peng and F.J. Wang
"Partially Averaged Navier-Stokes Modelling of
Turbulent Channel Flow with and without Forcing",
Turbulence, Heat and Mass Transfer 6,
K. Hanjalic, Y. Nagano and S. Jakirlic (Editors),
2009 Begell House, Inc., 2009.
View PDF file
-
J.M. Ma, L. Davidson, S.-H. Peng and F.J. Wang
"Partially Averaged Navier-Stokes Modelling of
Turbulent Channel Flow with and without Forcing",
Turbulence, Heat and Mass Transfer 6,
K. Hanjalic, Y. Nagano and S. Jakirlic (Editors),
2009 Begell House, Inc., 2009.
View PDF file
-
J.M. Ma, S.-H. Peng, L. Davidson and F. Wang
A Low Reynolds Number Partially-Averaged Navier-Stokes Model for Turbulence,
8th International ERCOFTAC Symposium on Engineering Turbulence, Modeling and Measurements,
Marseille, France, 9-11 June, 2010.
View PDF file
-
Ma, J.M, S.-H. Peng, L. Davidson and F.J. Wang
A low Reynolds number variant of partially-averaged Navier¿Stokes model
for turbulence, Int. J. Heat
Fluid Flow, Vol. 32, pp. 652-669,
2011.
Get article at publisher's www page
View PDF file of manuscript
|